A vulnerability in the web services interface of Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) Software and Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) Software could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker to conduct directory traversal attacks and read sensitive files on a targeted system. The vulnerability is due to a lack of proper input validation of URLs in HTTP requests processed by an affected. AnyConnect Plus/Apex licensing and Cisco head-end hardware is required. The application is not permitted for use with legacy licensing (Essentials or Premium PLUS Mobile). AnyConnect may not be used with non-Cisco hardware under any circumstances.
See the previous blog post which documents the steps to setup AnyConnect SSL-VPN and ISE integration. This blog post expands on the AnyConnect SSL-VPN configuration, adding support for IKEv2/IPSec and using double authentication (Username/Password and Certificate).
ASA Configuration
Create a Crypto Keypair
Create a CA Trustpoint
Authenticate the Trustpoint
In this example the ASA will enrol with a Windows Certificate Authority.
- Open the CA’s Trusted Root certificate in notepad
- Copy the contents on the certificate
- On the ASA run the command crypto ca authenticate LAB_PKI
- When prompted paste the contents of the CA Trusted Root certificate
- Type quit at the end
- Enter yes to import the certificate
EnrolL ASA for Identity Certificate
The ASA will create a CSR, which will need to be signed by the Windows CA and the signed certificate imported.
- On the ASA run the command crypto ca enroll LAB_PKI
- When prompted copy the contents of the CSR
- Complete the Certificate Signing Request
- On the Window CA open the Web page to sign certificates, click Request a certificate
- Click advanced certificate request
- Paste the CSR generated on the ASA in the previous step above
- Select the Certificate Template Web Server
- Click Submit
- Select Base 64 encoded
- Click Download certificate, save the file to a file for use in the next step
- On the ASA, run the command crypto ca import LAB_PKI certificate. LAB_PKI equals the name of the trustpoint previously defined.
- When prompted paste the contents of the saved file (generated in the previous step)
- Type quit at the end
- Verify the Identity and Trusted Root Certificates imported successfully by running the command show crypto ca certificates
- In the screenshot below the first certificate is the Identity Certificate (note the Subject name of the ASA). The second certificate is the Trusted Root certificate (note the subject name = lab=PKI-CA).
Enable the Certificate Trustpoint on the OUTSIDE interface
Enable the Certificate Trustpoint for Remote Access
Define IKEv2 Policy
Define IPSec Transform Sets
Define Crypto Map
Reference the previously created IPSec Transform Sets. Enable Crypto Map on OUTSIDE interface
Modify Group Policy to enable IKEv2
Enable AAA and Certificate authentication
For additional security double authentication will be configured to require certificate and username/password. The certificate will be authenticated against the ASA, the UN/PW will be authenticated against the RADIUS server (defined in the previous post).
Enable AAA accounting (if not already enabled)
AAA accounting should be enabled to keep track of the connections.
ISE Configuration
The ISE Authorization Policy as defined in the previous post needs modifying to add a new rule for clients connecting with IPSec. Using this attribute is optional, but can be used to distinguish between different connections types if required.

Cisco Ikev2 Troubleshooting
- Create a new Authorization rule called AnyConnect IPSec VPN
- Define Conditions: Cisco-VPN3000:CVPN3000/ASA/PIX7x-Tunnel-Group-Name CONTAINS TG-1 AND Cisco-VPN3000:CVPN3000/ASA/PIX7x-Client-Type EQUALS AnyConnect-Client-IPSec-VPN
- Permissions: VPN_Permit_DACL
Testing & Verification
You will need to create a AnyConnect Profile, download the AnyConnect Profile Editor
- Open the VPN Profile Editor
- Navigate to the Server List and click Add
- Define a display name for the connection e.g ASA IKEv2/IPSec VPN
- Define the FQDN
- Define the User Group, this represents the Tunnel-Group on the ASA, in this instance the name is TG-1 (as defined in the previous post)
- Set the Primary Protocol to IPSec
- Click Save and ensure the file is saved to the folder location:
- C:ProgramDataCiscoCisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility ClientProfile
- C:ProgramDataCiscoCisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility ClientProfile
- Restart the Cisco AnyConnect services or reboot
- Open the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client, this should display the new connection
The Windows computer has a User and Computer certificate issued by the same Windows CA that signed the certificate in use on the ASA, and therefore they should mutually trust each other and successfully authenticate.
Cisco Vpn Ikev2
- On the ASA run the command debug aaa authentication
- On the PC connect to the VPN and enter and username/password when prompted. Certificate authentication, if successful should be transparent
From the ASA debugs you can see the certificate authentication was successful
Authentication using Username/Password was also successful. You can see from the debug output aaa authentication was successful, a DACL was downloaded, aaa accounting was successful and the client was successfully assigned an IP address from the local pool.
- On the ASA run the command show vpn-session detail anyconnect
You will be able to confirm the Username, Assigned IP address, IKEv2 encryption algorithm used, authentication method, group-policy and tunnel-group etc.
Introduction
This document provides a sample configuration of how to configure an IOS/IOS-XE headend for remote access using AnyConnect IKEv2 and AnyConnect-EAP authentication method with local user database.
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- IKEv2 protocol
Components Used
The information in this document is based on these software and hardware versions:
- Cisco Cloud Services Router running IOS XE 16.9.2
- AnyConnect client version 4.6.03049 running on Windows 10
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Background Information
AnyConnect-EAP, also known as aggregate authentication, allows a Flex Server to authenticate the AnyConnect client using the Cisco proprietary AnyConnect-EAP method. Unlike standard based Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) methods such as EAP-Generic Token Card (EAP-GTC), EAP- Message Digest 5 (EAP-MD5) and so on, the Flex Server does not operate in EAP pass-through mode. All EAP communication with the client terminates on the Flex Server and the required session key used to construct the AUTH payload is computed locally by the Flex Server. The Flex Server has to authenticate itself to the client using certificates as required by the IKEv2 RFC.
Local user authentication is now supported on the Flex Server and remote authentication is optional. This is ideal for small scale deployments with less number of remote access users and in environments with no access to an external Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) server. However, for large scale deployments and in scenarios where per-user attributes are desired it is still recommended to use an external AAA sever for authentication and authorization. The AnyConnect-EAP implementation permits the use of Radius for remote authentication, authorization and accounting.
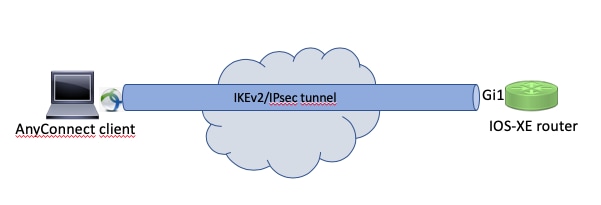
Network Diagram
Configure
Authenticating and Authorizating users using the Local Database
Note: In order to authenticate users against the local database on the router, EAP needs to be used. However, in order to use EAP, the local authentication method has to be rsa-sig, so the router needs a proper certificate installed on it, and it can't be a self-signed certificate.
Sample configuration that uses local user authentication, remote user and group authorization and remote accounting.
Step 1. Enable AAA, and configure authentication, authorization and accounting lists and add a username to the local database:
Step 2. Configure a trustpoint that will hold the router certificate. PKCS12 file import is used in this example. For other options, please consult the PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) configuration guide:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_conn_pki/configuration/xe-3s/sec-pki-xe-3s-book/sec-cert-enroll-pki.html
Step 3. Define an IP local pool to assign addresses to AnyConnect VPN clients:
Step 4. Create an IKEv2 local authorization policy:
Step 5 (Optional). Create desired IKEv2 proposal and policy. If not configured, smart defaults will be used:
Business in a box hack. Step 6. Create AnyConnect profile
Cisco Asa Debug Ikev2
Note: The AnyConnect profile needs to be delivered to the client machine. Please refer to the next section for more information.
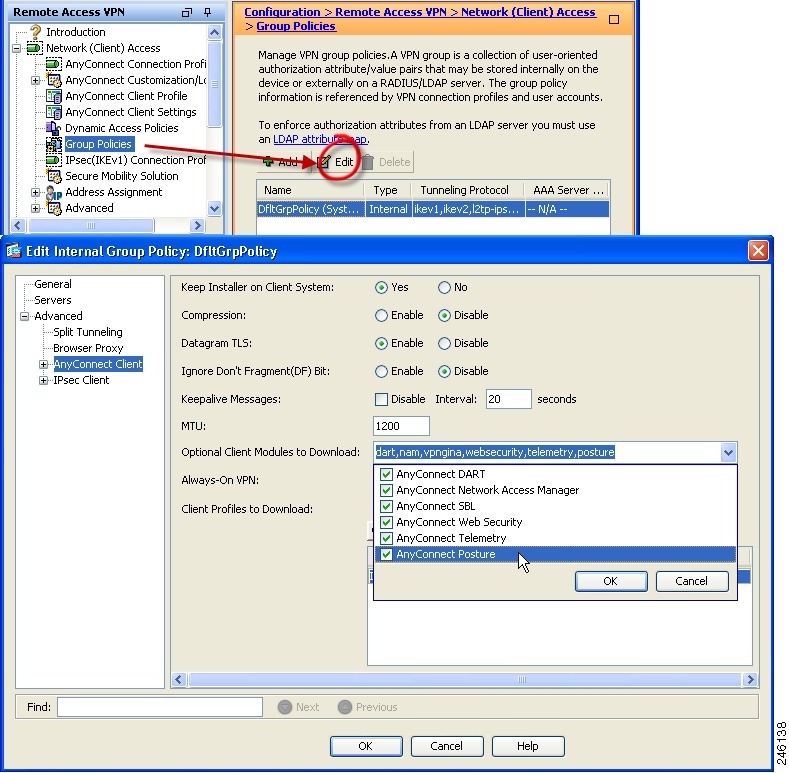
Configure the client profile using the AnyConnect Profile Editor as shown in the image:
Click 'Add' to create an entry for the VPN gateway. Make sure to select 'IPsec' as 'Primary Protocol'. Uncheck the 'ASA gateway' option.
Save the profile by going to FIle -> Save As. The XML equivalent of the profile:
Note: AnyConnect uses '*$AnyConnectClient$*' as its default IKE identity of type key-id. However, this identity can be manually changed in the AnyConnect profile to match deployment needs.
Note: In order to upload the XML profile to the router, IOS-XE 16.9.1 version or later is required. If older version of IOS-XE software is used, the profile download capability needs to be disabled on the client. Please refer to the section 'Disabling the AnyConnect downloader capability' for more information.
Upload the created XML profile to the flash memory of the router and define the profile:
Note: The filename used for AnyConnect XML profile should be acvpn.xml.
Step 7. Create an IKEv2 profile for AnyConnect-EAP method of client authentication.
Note: Configuring the remote authentication method before the local authentication method will be accepted by the CLI, but will not take effect on versions that do not have the fix for the enhancement request CSCvb29701, if the remote authentication method is eap. For these versions, when configuring eap as the remote authentication method, ensure the local authentication method is configured as rsa-sig first. This problem is not seen with any other form of remote authentication method.
Note: On versions of code affected by CSCvb24236 , once remote authentication is configured before local authentication, the remote authentication method can no longer be configured on that device. Please upgrade to a version that has the fix for this code.
Step 8. Disable HTTP-URL based certificate lookup and HTTP server on the router:
Note: Referthis document to confirm whether your router hardware supports the NGE encryption algorithms (for example the example above has NGE algorithms). Otherwise IPSec SA installation on the hardware will fail at the last stage of negotiation.
Step 9. Define the encryption and hash algorithms used to protect data
Step 10. Create an IPSec profile:
Step 11. Configure a loopback interface with some dummy IP address. The Virtual-Access interfaces will borrow the IP address from it.
Step 12. Configure a virtual-template (associate the template in the IKEv2 profile)
Steap 13 (Optional). By default, all traffic from the client will be sent through the tunnel. You can configure split tunnel, which allows only selected traffic to go through the tunnel.
Cisco Anyconnect Download
Step 14 (Optional). Redis client mac gui. If all traffic is required to go through the tunnel, you may configure NAT in order to allow internet connectivity for remote clients.
Disabling the AnyConnect downloader capability (optional).
This step is only necessary if IOS-XE software version older than 16.9.1 is being used. Prior to IOS-XE 16.9.1 the capability to upload the XML profile to the router was not available. The AnyConnect client tries to perform download of the XML profile after successful login by default. If the profile is not available, the connection fails. As a workaround, it is possible to disable the AnyConnect profile download capability on the client itself. In order to do that, the following file can be modified:
The 'BypassDownloader' option should be set to 'true', for example:
After the modification, the AnyConnect client needs to be restarted.
AnyConnect XML profile delivery
With the fresh installation of the AnyConnect (with no XML profiles added), the user is able to manually enter the FQDN of the VPN gateway in the address bar of AnyConnect client. This results in the SSL connection to the gateway. The AnyConnect client will not attempt to establish the VPN tunnel with IKEv2/IPsec protocols by default. Bluestacks 1 app player download. This is the reason why having XML profile installed on the client is mandatory to establish the IKEv2/IPsec tunnel with IOS-XE VPN gateway.
The profile is used when it is being selected from the drop-down list of AnyConnect address bar. The name that will appear is the same name as specified in 'Display Name' in AnyConnect profile editor. In this example the user should select the following:
The XML profile can be manually put into the following directory:
The AnyConnect client needs to be restarted in order for the profile to become visible in the GUI. It's not sufficient to close the AnyConnect window. The process can be restarted by right-clicking AnyConnect icon in the Windows tray and selecting 'Quit' option:
Communication flow
Cisco Anyconnect Ikev2 License
IKEv2 and EAP exchange
Verify
Use this section in order to confirm that your configuration works properly.
Troubleshoot
This section provides information you can use in order to troubleshoot your configuration.
- IKEv2 debugs to collect from the headend:
- AAA debugs to see assignment of local and/or remote attributes:
- DART from the AnyConnect client.




